DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) works in a client/server mode. DHCP enables clients on an IP network to obtain or lease IP address or configuration from a DHCP server. This reduces workload when managing a large network. DHCP protocol is described in the RFC 2131.
Most modern operating system includes DHCP in their primary settings, these includes windows OS, Novell NetWare, Sun Solaris, Linux and Mac OS. The clients’ requests for addressing configuration from a DHCP network server, the network server manages the assignment of IP addresses and must be obliged to answer to any IP configuration requests from clients.
However, network routers, switches and servers need to have a static IP addresses, DHCP is not intended for the configuration of these types of hosts. Cisco routers use a Cisco IOS features known as Cisco Easy IP Lease. This offers an optional but full-featured DHCP server. Easy IP leases address for 24hrs by default, it is most useful in homes and small offices where users can take the advantages of DHCP and NAT without having an NT or UNIX server
The DHCP sever uses User Datagram Protocol (UTP) as it’s transport protocol to send message to the client on port 68, while the client uses port 67 to send messages to the server.
DHCP severs can offer other information, this include, DNS server addresses, WINS server addresses and domain names. In most DHCP servers, administrators are allowed to define clients MAC addresses, which the server automatically assigns same IP, address each time.
Most administrators prefer to work with Network server that offers DHCP services. These types of network are scalable and easy to manage.
How DHCP Operates
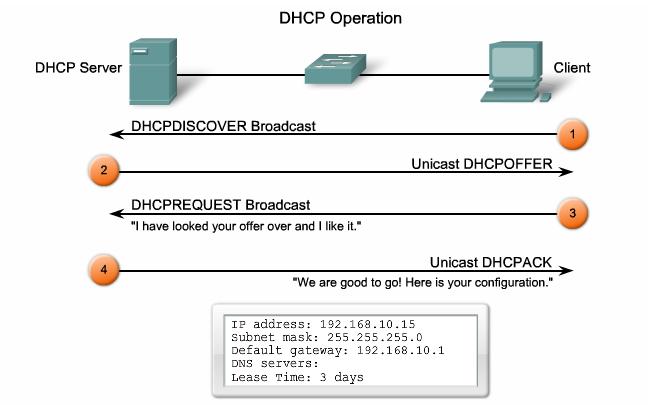
DHCP server’s most fundamental task is Providing IP addresses to clients. DHCP uses three different address allocation mechanisms when assigning IP addresses:
Manual Allocation: The administrator manually assigns a pre-allocated IP address to the client and DHCP only communicates the IP address to the device.
Automatic Allocation: DHCP automatically assigns a static IP address permanently to a device, selecting it from a pool of available addresses. There is no lease and the address is permanently assigned to a device.
Dynamic Allocation: DHCP automatically dynamically assigns, or leases, an IP address from a pool of addresses for a limited period of time chosen by the server, or the address will be withdrawn when the client tells the DHCP server that it no longer needs the address.
Dynamic IP address allocation
DHCP works in a client/server mode and operates like any other client/server relationship. When a PC connects to a DHCP server, the server assigns or leases an IP address to that PC, which enables The PC, connects to the network with that leased IP address until the lease expires. The host must contact the DHCP server intermittently to extend the lease. This lease mechanism ensures that hosts / clients that are mobile or power off do not hold onto addresses that they do not need. These addresses are return back to the pool by the to be reallocated to other clients when needed.
Dynamically assigning Client IP Addresses via DHCP on Cisco Router
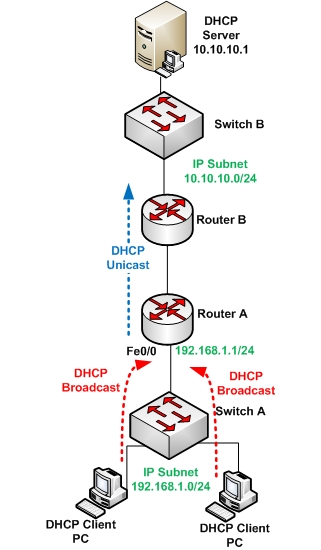
DHCP assigns IP addresses and other important network configuration information to clients dynamically. Cisco router uses the Cisco IOS feature known as Easy IP as an optional DHCP server. Easy IP leases IP configurations to network clients for 24 hours by default. We use the topology diagram below as sample network topology.
Step1. Configure excluded address(es): These addresses are reserved for network hosts or clients that need Static Addresses, such as servers, routers and printers. These IP addresses are not included in the address pools that are available for assigning to other clients.
DHCP excluded address on R1:
R1#config terminal
R1(config)#ip dhcp excluded-address 192.168.30.1 192.168.30.9
R1(config)#end
R1#
Step2. Configure the address pool: Define the pool of addresses from which DHCP assigns addresses to clients on the network. in this case (R1) the available addresses are all addresses on the 192.168.30.0 network, except for the range excluded on step 1.
Configure address pool on R1: define the address pool, default gateway, and DNS server that are assigned to each client requesting for DHCP IP configuration.
R1(config)#ip dhcp pool R1LAN
R1(dhcp-config)#network 192.168.30.0 255.255.255.0
R1(dhcp-config)#default-router 192.168.30.1
R1(dhcp-config)#dns-server 192.168.10.254
R1(dhcp-config)#end
R1#
Do the same on R3 in this case:
Excluded address for R3:
R3(config)#ip dhcp excluded-address 192.168.20.1 192.168.20.9
R3(config)#end
R3#
Address pool for R3:
R3(config)#ip dhcp pool R3LAN
R3(dhcp-config)#network 192.168.20.0 255.255.255.0
R3(dhcp-config)#default-router 192.168.20.1
R3(dhcp-config)#dns-server 192.168.10.254
R3(dhcp-config)#end
R3#
More related: Cisco Catalyst 4500 Switch, How to Configure a DHCP Relay on It?
More Cisco Reading: Understanding and Troubleshooting DHCP in Catalyst Switch or Enterprise Networks