There are several ways you can verify and troubleshoot OSPF configuration and operation, listed below are the necessary command to do this:
How to verify OSPF Configuration:
Show IP route command
Show IP ospf command
Show ip ospf database command
Show ip ospf interface command
Show ip ospf neighbour command
Show ip protocols command
Debugging ospf
The Show IP route command:
R1#sho ip route
10.0.0.0/30 is subnetted, 3 subnets
C 10.1.1.0 is directly connected, Serial0/0/1
O 10.10.10.0 [110/128] via 10.20.20.2, 00:05:14, Serial0/0/0
[110/128] via 10.1.1.2, 00:05:14, Serial0/0/1
C 10.20.20.0 is directly connected, Serial0/0/0
172.16.0.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnets
O 172.16.10.0 [110/65] via 10.1.1.2, 00:05:14, Serial0/0/1
O 192.168.1.0/24 [110/65] via 10.20.20.2, 00:07:38, Serial0/0/0
C 192.168.20.0/24 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0
R1#
Using the the above command displays all routes on the network, with the O representing the OSPF internal routes. The Cs are directly connected networks. It also found the dual route to the 10.10.10.0 network.
Using the show OSPF Command
Another way of troubleshooting and verifying OSPF configuration is by using the Show IP ospf command; the following information will be displayed:
R1#show ip ospf
Routing Process “ospf 1” with ID 192.168.20.1
Supports only single TOS(TOS0) routes
Supports opaque LSA
SPF schedule delay 5 secs, Hold time between two SPFs 10 secs
Minimum LSA interval 5 secs. Minimum LSA arrival 1 secs
Number of external LSA 0. Checksum Sum 0x000000
Number of opaque AS LSA 0. Checksum Sum 0x000000
Number of DCbitless external and opaque AS LSA 0
Number of DoNotAge external and opaque AS LSA 0
Number of areas in this router is 1. 1 normal 0 stub 0 nssa
External flood list length 0
Area BACKBONE(0)
Number of interfaces in this area is 3
Area has no authentication
SPF algorithm executed 7 times
Area ranges are
Number of LSA 3. Checksum Sum 0x012733
Number of opaque link LSA 0. Checksum Sum 0x000000
Number of DCbitless LSA 0
Number of indication LSA 0
Number of DoNotAge LSA 0
Flood list length 0
R1#
The above command displays OSPF information all ospf processes running on the router. Here you can find out the router ID, area information, SPF statistics and LSA timers information…
The Show IP OSPF Database Command
Show ip ospf database: This command can be used during network troubleshooting.
R1#show ip ospf database
OSPF Router with ID (192.168.20.1) (Process ID 1)
Router Link States (Area 0)
Link ID ADV Router Age Seq# Checksum Link count
192.168.1.1 192.168.1.1 1321 0x80000005 0x0042ab 5
192.168.20.1 192.168.20.1 1281 0x80000005 0x00826a 5
172.16.10.1 172.16.10.1 1281 0x80000005 0x00621e 5
This command displays the information on the number of routers in the network or internetwork plus the neighboring routers ID.
Here you can see three routers with their various IDs (which is the highest IP on each router). Also you can see the link ID. The ADV router is the advertising router. The checksum link count might display different numbers depending on the routing device.
Show ip ospf interface command explained.
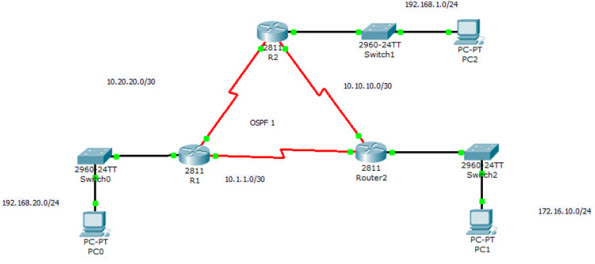
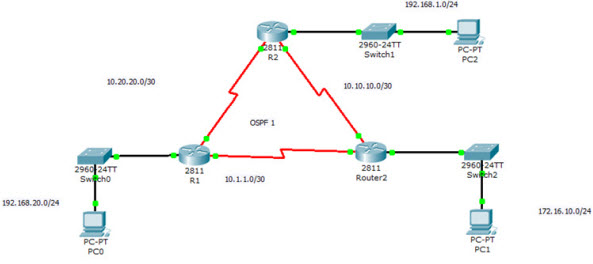
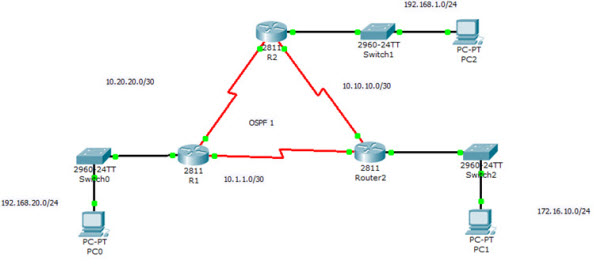
We use the following topology for demonstration.
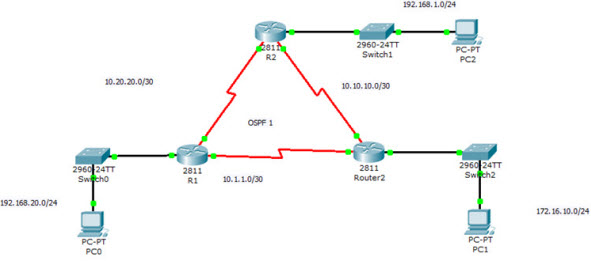
The show ip ospf interface command on R1, will display the following output:
R1#show ip ospf interface fa0/0
FastEthernet0/0 is up, line protocol is up
Internet address is 192.168.20.1/24, Area 0
Process ID 1, Router ID 192.168.20.1, Network Type BROADCAST, Cost: 1
Transmit Delay is 1 sec, State DR, Priority 1
Designated Router (ID) 192.168.20.1, Interface address 192.168.20.1
No backup designated router on this network
Timer intervals configured, Hello 10, Dead 40, Wait 40, Retransmit 5
Hello due in 00:00:06
Index 1/1, flood queue length 0
Next 0x0(0)/0x0(0)
Last flood scan length is 1, maximum is 1
Last flood scan time is 0 msec, maximum is 0 msec
Neighbor Count is 0, Adjacent neighbor count is 0
Suppress hello for 0 neighbor(s)
Serial0/0/0 is up, line protocol is up
Internet address is 10.20.20.1/30, Area 0
Process ID 1, Router ID 192.168.20.1, Network Type POINT-TO-POINT, Cost: 64
Transmit Delay is 1 sec, State POINT-TO-POINT, Priority 0
No designated router on this network
No backup designated router on this network
Timer intervals configured, Hello 10, Dead 40, Wait 40, Retransmit 5
Hello due in 00:00:02
Index 2/2, flood queue length 0
Next 0x0(0)/0x0(0)
Last flood scan length is 1, maximum is 1
Last flood scan time is 0 msec, maximum is 0 msec
Neighbor Count is 1 , Adjacent neighbor count is 1
Adjacent with neighbor 192.168.1.1
Suppress hello for 0 neighbor(s)
The above command displays the following information on each router interface:
i. Area assignment
ii. Interface IP address
iii. Process ID
iv. Router ID
v. Network type
vi. Cost
vii. Priority
viii. DR/BDR election information hello and dead timer intervals
ix. Adjacent neighbour information
The Show ip ospf neighbour command:
R1#show ip ospf neighbor
Neighbor ID Pri State Dead Time Address Interface
192.168.1.1 0 FULL/ – 00:00:33 10.20.20.2 Serial0/0/0
172.16.10.1 0 FULL/ – 00:00:32 10.1.1.2 Serial0/0/1
R1#
The above command displays the summary of ospf information regarding and the adjacency state. This command is very useful on a production network.
The Show IP protocols command:
This command display the following information
R1#show ip protocols
Routing Protocol is “ospf 1”
Outgoing update filter list for all interfaces is not set
Incoming update filter list for all interfaces is not set
Router ID 192.168.20.1
Number of areas in this router is 1. 1 normal 0 stub 0 nssa
Maximum path: 4
Routing for Networks:
192.168.20.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
10.20.20.0 0.0.0.3 area 0
10.1.1.0 0.0.0.3 area 0
Routing Information Sources:
Gateway Distance Last Update
172.16.10.1 110 00:14:00
192.168.1.1 110 00:14:40
192.168.20.1 110 00:14:00
Distance: (default is 110)
R1#
This command is used to verify the type of protocols running on your router and network. The display above shows the OSPF process ID, OSPF router ID, type of OSPF area, networks and areas configured for OSPF neighboring router’s ID etc…etc.
The Debugging OSPF Command:
Among information provided by this command is the:
i. Debug ip ospf packet: this command displays hello packets being sent and received on your router
ii. Debug ip ospf hello: this command displays hello packets being sent and received on your router. It also displays more information than the debug ospf packet
iii. The debug ip ospf adj: shows DR and DBR elections on a broadcast and non-broadcast multi-access (NBMA) network.
—Guide Reference from https://www.orbit-computer-solutions.com
More Related Readings:
Troubleshooting OSPF
https://www.cisco.com/en/US/tech/tk365/technologies_tech_note09186a00800949f7.shtml