There are several topics about the Cisco ISR 4000 series, such as Benefits You Get from Migrating to Cisco 4000 Series ISR…,Cisco ISR 4451-X, Prepared for Future Branch Network Needs, Cisco 4000 Series ISR, Top Choice for Today’s Branch Offices, Cisco 4451-X vs. Cisco 3945E vs. 3925E vs. Cisco 3945 vs. 3925 Router, New Cisco NIM cards for Cisco ISR 4000 Family, etc. 
It seems that the Cisco 4000 Series is the best New Integrated Services Router for distributed organizations with multiple branch offices and remote sites.
The Cisco 4000 Series ISRs build on 20 years of branch-office routers, adding services and horsepower for the needs of modern branch offices and allowing businesses to:
- Quickly open new remote offices or easily add additional services
- Operate an entire branch office with a single box
- Give IT departments more time for innovation by automating repetitive tasks and orchestrating security and application services
In this article we will talk about the 2 main series of Cisco ISR 4000 Family: The Cisco 4400 and 4300 Series ISRs.
The Cisco 4400 and 4300 Series ISRs are very similar in design user interface. The biggest difference to most users is that the Cisco 4400 Series supports dual power supplies, whereas the Cisco 4300 Series does not; this difference makes the Cisco 4451 and 4431 the preferred choices for organizations that cannot tolerate any downtime.
The 4400 Series routers have a physical separation between control and data planes, and they use dedicated CPU sockets for each. The Cisco 4300 Series uses a single socket with multiple CPU cores allocated to the control plane, data plane, and services, a difference most users would never be aware of.
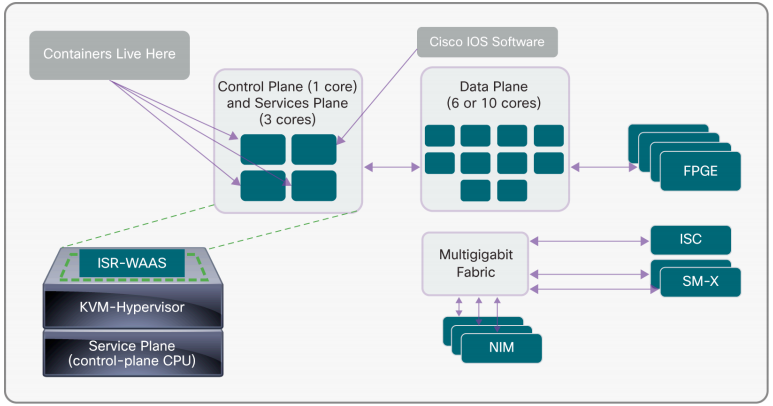
Figure1. shows the Cisco 4400 Series architecture.
- ● FPGE: Front-Panel Gigabit Ethernet–The Ethernet interfaces on the front panel.
- ● ISC: Internal Services Card–An internal module used for exmanding the capabilities of the system. Commonly used for DSP modules.
- ● SM-X: Enhanced Service Module–A larger module type used mainly for UCS E-Series server blades and high density Ethernet switch modules.
- ● NIM: Network Interface Module–Half the size of an SM-X generally used for WAN, Voice and low-density Ethernet interfaces.
The Cisco 4400 Series uses two multicore CPU complexes for the data plane (packet processing) and control and services planes. In Cisco IOS XE Software, classic Cisco IOS Software runs as a single daemon within a Linux OS, helping ensure control-plane protocol compatibility with all other Cisco routers; this setup is indicated as “Cisco IOS Software” in the figure. Additional system functions now run as additional, separate processes in the host OS environment. “ISR-WAAS” in the figure is virtualized Cisco Wide Area Application Services (WAAS) in a Cisco IOS XE Software service container. As with previous generations of Cisco routers, a multigigabit fabric supports intercommunication among the IP Solution Center (ISC), Cisco SM-X EtherSwitch Modules, and network interface modules (NIMs).
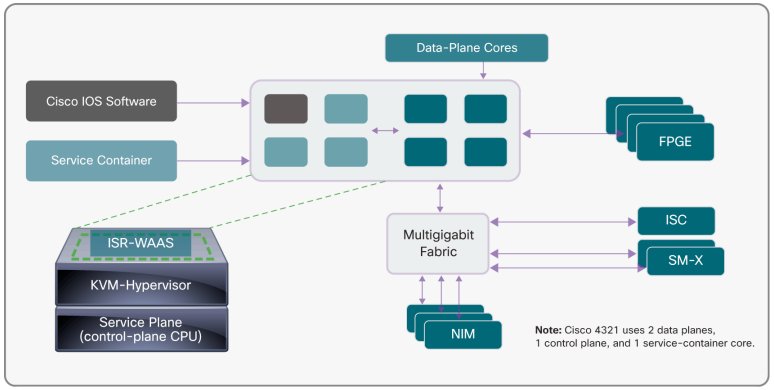
Figure2 shows the Cisco 4300 Series architecture, which is similar to the 4400 model but does not include physical separation of the control and data planes. All functions are exactly the same, with identical end-user experiences and feature support.
Figure2. Cisco 4300 Series Architecture
Individual Models in the Cisco 4000 Series
Figure3 shows the Cisco 4451 Integrated Services Router.
Figure3. Cisco 4451
The Cisco 4451 is suggested for migration from the existing Cisco 3925E and 3945E routers. It offers 1-Gbps performance, upgradable to 2 Gbps, in a 2-rack-unit (2RU) form factor with 3 network interface module (NIM) slots and 2 enhanced service module (SM-X) slots. It includes an option for redundant power.
- 4-core processors (1 control and 3 services processors)
- 10-core data plane
- Single or double-wide Cisco UCS E-Series support
- Up to 16-GB control and services memory
Figure4 shows the Cisco 4431 Integrated Services Router.
Figure4. Cisco 4431
The Cisco 4431 is suggested for migration from the existing Cisco 3925 and 3945 routers. It offers 500-Mbps performance, upgradable to 1 Gbps, in a 1RU form factor with 3 NIM slots and no SM slots. It includes an option for redundant power.
- 4-core processors (1 control and 3 services)
- 6-core data plane
- Up to 16-GB control and services memory
Figure5 shows the Cisco 4351 Integrated Services Router.
Figure5. Cisco 4351
The Cisco 4351 is suggested for migration from existing Cisco 2951 routers. It offers 200-Mbps performance, upgradable to 400 Mbps, in a 2RU form factor with 3 NIM slots and 2 SM slots.
- 8-core CPU with 4 data-plane cores, 1 control-plane core, and 3 cores dedicated for services
- Single or double-wide Cisco UCS E-Series support, and up to 16-GB control and services memory
Figure6 shows the Cisco 4331 Integrated Services Router.
Figure6. Cisco 4331
The Cisco 4331 is suggested for migration from the existing Cisco 2911 and 2921 routers. It offers 100-Mbps performance, upgradable to 300 Mbps, in a 1RU form factor with 2 NIM slots and 1 SM slot.
- 8-core CPU with 4 data-plane cores, 1 control-plane core, and 3 cores dedicated for services
- Single-wide Cisco UCS E-Series support, and up to 16-GB control and services memory
Figure7 shows the Cisco 4321 Integrated Services Router.
Figure7. Cisco 4321
The Cisco 4321 is suggested for migration from the existing Cisco 2901 and 1941 routers. It offers 50-Mbps performance, upgradable to 100 Mbps, in a 1RU desktop form factor with 2 NIM slots and no SM slots.
- 4-core CPU with 2 data-plane cores, 1 control-plane core, and 1 core dedicated for services
- Up to 8-GB control and services memory
The Cisco 4000 Series is designed to help branch and remote offices do more with less. These routers mean more bandwidth and intelligent WAN management, and also more virtual machines, more data center–class servers, and more flexibility in upgrading. And they mean less need for rack space; lower cost for maintenance, power, and cooling; and less time spent by IT staff managing routers. The Cisco 4000 Series is available now for ordering.
More about the Key Features of the Cisco 4000 Series ISRs
The Cisco 4000 Series ISRs include several important features that make it a perfect choice for today’s branch offices:
- Price for performance: The Cisco 4000 Series allows branch offices to handle increased bandwidth using a single box without the need for security and optimization appliances, helping control costs. The platform is manageable for a small IT staff. The platforms run concurrent Intelligent WAN (IWAN) services, including security, application optimization, AVC, and intelligent path selection. The price for performance extends to the physical design: The 4000 Series ISRs use more compact boxes than previous-generation Cisco branch-office routers; and they include an industry-first altitude sensor, which helps ensure that the fans spin at the optimal speed, thereby reducing noise pollution in the office.
- Performance on demand (pay as you grow): Branch offices can upgrade to a higher level of bandwidth without having to buy a new box. Each model in the Cisco 4000 Series offers additional performance and services that you can activate remotely with a license. For example, a branch office can implement a Cisco 4351 with a baseline performance of 200 Mbps. But when a new application rollout increases the need for bandwidth, you can boost the performance (up to 400 Mbps for the Cisco 4351) with no additional hardware, at a fraction of the cost of buying a new router, and no expensive upgrades are required.
- Services on demand: Service containers allow virtual machines to run within the Cisco 4000 Series. Essential branch-office services that the branch office is already running, such as WAN optimization and energy management, can run natively on the router. Thus the branch office can consolidate servers and appliances, reducing its hardware footprint and power usage.
- Scalable services: The Cisco 4000 Series routers support Cisco Unified Computing System (Cisco UCS) E-Series Blade servers, which are comparable to a full-size server. The blades use the power supply and chassis of the router, but are managed separately from the router; resetting a blade will not reset the router and the network team members don’t have to give their passwords to the server team. This setup gives an IT department all the benefits of a separate data center–class server without the need for maintaining another box. In addition, a separate server virtual-machine license is not required, and troubleshooting involves only one point of contact instead of multiple vendors, resulting in better uptime and reliability. As an added bonus, hardware support costs through Cisco SMARTnet support are bundled into the router support cost. Any Cisco UCS E-Series servers hosted in an ISR are covered at no additional fee. This is beneficial because those support fees can really add up when dealing with potential hard-drive failures in a server.
More Related…
Migrating to Cisco 4000 Series ISR…Benefits You Get
Cisco 4451-X vs. Cisco 3945E vs. 3925E vs. Cisco 3945 vs. 3925 Router
Cisco 4000 Series ISR, Top Choice for Today’s Branch Offices
New Cisco NIM cards for Cisco ISR 4000 Family
Ordering Guide-Cisco 4400 and 4300 Series Routers/Cisco 4000 Router Family