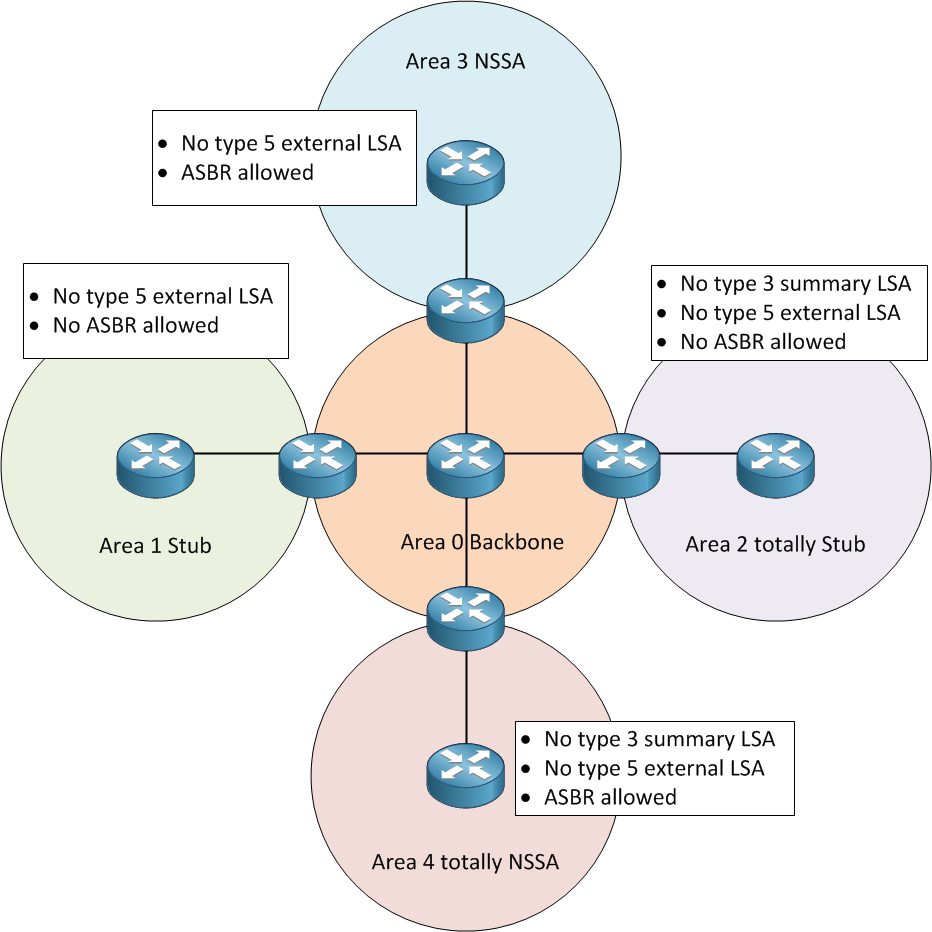
In the intricate world of computer networking, the Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) protocol reigns supreme. OSPF is a vital component for routing data across networks, and it operates within designated areas, each with a distinct role. In this article, we delve into the five OSPF area types, shedding light on their unique functions and significance in network design.
1. Backbone Area (Area 0): The Central Nerve of OSPF
Imagine the OSPF network as a complex web of interconnected nodes. In this web, the Backbone Area, often referred to as Area 0, plays a pivotal role. By OSPF design principles, Area 0 acts as the central hub in the OSPF network. It serves as the linchpin for transmitting link information from other areas. In essence, all other areas must be connected to Area 0 to ensure seamless data exchange. The Backbone Area supports various types of Link State Advertisements (LSAs), including Type 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5.
2. Standard Area: Normal Data Transfer
The Standard Area, often known as the standard area, functions as an area where OSPF packets are transmitted without restrictions. Just like the Backbone Area, the Standard Area supports a wide array of LSAs, including Type 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5.
3. Stub Area: Simplified Routing
The Stub Area lives up to its name by simplifying routing. This area is unique because it does not accept external routes from non-OSPF networks. Instead, if it needs to reach external routes, it forwards them using the default route. The Stub Area primarily supports LSAs of Type 1, 2, and 3.
4. Totally Stubby Area: Streamlined and Secure
The Totally Stubby Area takes simplification a step further. This area not only refrains from accepting external routes but also refuses to accept link information from areas outside its domain. To reach networks beyond the area, it employs the use of default routes, similar to the Stub Area. However, it’s important to note that the Totally Stubby Area does not allow ordinary Type 3 LSA packets. Instead, it supports this LSA type with default routes. This area accommodates Type 1, Type 2 LSAs, and Type 3 LSAs with default routes.
5. Not So Stubby Area (NSSA): Versatility Amid Simplicity
The Not So Stubby Area, often referred to as NSSA, is a hybrid entity that emerges from the concept of a Stub Area. It maintains the simplicity of a stub area but also has the capability to send external routes to other areas. The NSSA supports a mix of LSAs, including Type 1, 2, 3, and 7. It’s worth mentioning that there is another variation, known as the NSSA of the Totally Stubby Area mode. This mode, despite being in a completely stubby area environment, allows the introduction of external routes.
These OSPF area types are like puzzle pieces in network design. The choice of area type is crucial and should align with the specific network’s requirements and topology.
Are you seeking networking solutions that align with your OSPF design and implementation? Router-switch.com has you covered. As a premier destination for networking products and solutions, our platform offers a plethora of options to meet your unique needs.
Visit Router-switch.com for Networking Excellence
Router-switch.com stands out as a one-stop solution for all your networking needs. Whether you’re designing an OSPF network or seeking the latest networking products, we have the expertise and products to support your journey.
Read More:
Only in Q4: 2023 Router-Switch.com Season Sale Customer Benefits
Expand Your Business Horizons by Becoming a Supplier of Router-switch.com