The Value of Infiniband
Infiniband and Related Technical Background
- Ethernet: Started in 1973, the most popular and successful network ecosystem to date, widely used for interconnecting computers.
- Infiniband: Started in 1999, it is the best performing network system, and this technology is designed for high-performance application scenarios.
- RoCE: Started in 2010, the transplantation of IB RDMA features on Ethernet technology
Image Source: Pexels
Infiniband Core Value
Highest application performance
- High bandwidth (Gbps)
- Low latency (ns/p2p, ns/hop)
- High packet throughput (Mpps)
- Network computing-SHARP (4x better in MPI latency)
Maximized CPU utilization
Unload CPU workload, no need for CPU to intervene in data plane processing-Native RDMA
Optimal network utilization
Availability (HA) = SHIELD/adaptive routing/congestion control
Scalability-native software-defined network, centralized management, network scale expansion without additional overhead
Infiniband Performance Advantages
Hardware Dimensions
| lantency | IB (ConnectX-6 HDR) | RoCE (ConnectX-6 Dx 200GE) | TCP/IP (ConnectX-6 Dx 200GE) |
| Back-to-back interconnection | ~700ns | ~900ns | 4000-5000ns |
| Through the switch | 700 + ~130ns | 900+ ~300ns | 5000+ ~300ns |
| Bandwidth vs CPU usage | IB (ConnectX-6 HDR) | RoCE (ConnectX-6 Dx 200GE) | TCP/IP(ConnectX-6 Dx 200GE) |
| CPU cores occupied | 1 core | 1 core | 24 cores |
| Bandwidth | 197Gbps | 189Gbps | 190Gbps |
Software Dimension
- In-Network Computing-SHARP feature reduces latency brought by distributed computing
- SHIELD-fast network link self-repair, improve network availability
- Adaptive Routing-optimal network routing selection, reduce latency and congestion
Image Source: NVIDIA
Ecological Dimension
- HPC TOP500 ranking leading network technology supplier
- Open MPI based HPC-X/UCX, a large cluster communication framework widely verified in the HPC/AI field
- Practices on 6000*32(N*PPN) cluster, based on HPC-X 2.7/UCX 1.9/Slurm 20.11 in China domestic customer
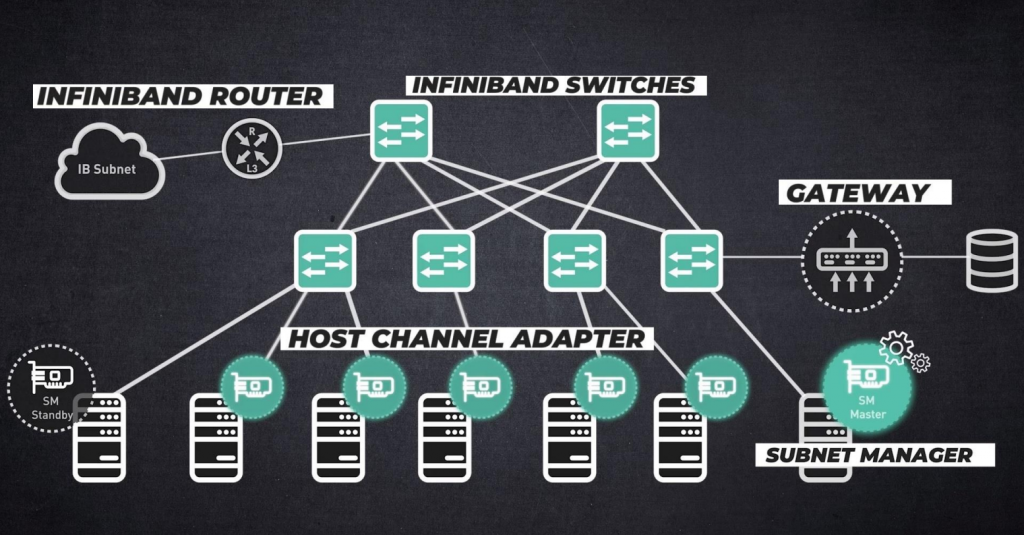
Infiniband Products
IB card/nvidia infiniband switches/router/gateway
Image Source: NVIDIA
(Read “NVIDIA Networking – InfiniBand Solutions” for additional information)
Network Management Tool – UFM (Unified Fabric Manager)
UFM Telemetry
A component of NVIDIA’s Unified Fabric Manager (UFM) that specializes in detailed network monitoring and performance data collection.
- Real-time Data Collection: Gathers real-time metrics such as bandwidth, latency, and packet loss.
- Visualization: Offers tools for visualizing network performance through charts and reports.
- Historical Data Storage: Stores historical performance data for trend analysis.
Alert Mechanism: Sends automated alerts for anomalies or performance bottlenecks.
UFM Enterprise
Designed for large-scale enterprises and data centers, providing comprehensive network management and optimization features.
- Centralized Management: Unified platform for monitoring and managing the entire network infrastructure.
- Automated Configuration: Reduces complexity and human error through automated network configuration.
- High Scalability: Capable of managing thousands of nodes in large network environments.
- Performance Optimization: Continuously monitors and optimizes network performance.
- Comprehensive Reporting: Generates detailed reports on network health and performance.
UFM Cyber AI
An advanced security module within UFM that leverages artificial intelligence to enhance network security and reliability.
- Anomaly Detection: Uses AI and machine learning to identify abnormal behaviors and potential security threats.
- Automated Protection: Automatically implements countermeasures like blocking suspicious traffic or isolating compromised nodes.
- Threat Intelligence: Integrates up-to-date threat intelligence to combat new types of attacks.
- Security Reporting: Provides detailed reports on security incidents for analysis.
- Continuous Learning: AI models continuously learn and adapt to evolving threats. (Read “NVIDIA Unified Fabric Manager (UFM)” for additional information)
Infiniband key features:
Lossless
- Physical: Lower bit error rate target 10e-15 (1000 times that of Ethernet)
- Link: Credit-based port-to-port flow control to ensure sufficient buffer on the receiving side and no active packet loss
Image Source: NVIDIA
SHARP (Scalable Hierarchical Aggregation and Reduction Protocol)
It is a technology used to improve communication efficiency in high-performance computing (HPC) and artificial intelligence (AI) applications. It mainly improves the overall performance of computing clusters by optimizing data aggregation and reducing communication overhead.
Specifically, SHARP technology plays a key role in the following aspects:
- Data aggregation: In a distributed computing environment, many operations require data from multiple nodes to be aggregated together, such as gradient aggregation in deep learning. SHARP reduces the transmission time and bandwidth consumption of data in the network by implementing these aggregation operations in the network layer.
- Hierarchical communication: SHARP adopts a hierarchical communication strategy to effectively utilize the network topology. For example, in a multi-level switch structure, SHARP can perform partial data processing on the switch node, reducing the amount of data transmitted to the computing node.
- Hardware acceleration: SHARP implements some key operations on the network hardware, such as directly supporting these aggregation and reduction operations on nvidia InfiniBand switches, which avoids multiple transmissions of data in the network and improves overall communication efficiency.
- Scalability: SHARP was designed to work in large clusters, and by optimizing communication patterns, it can remain efficient when scaled to thousands or even tens of thousands of nodes.
Adaptive routing
NVIDIA Adaptive Routing is an advanced networking technology designed to optimize data flow in high-performance computing (HPC) and data center environments.
- Dynamic Path Selection:
It dynamically selects the most efficient path for data packets to travel through the network. This selection is based on real-time traffic conditions and network congestion.
- Real-Time Monitoring:
The technology continuously monitors the status of the network, allowing it to make informed decisions on the best paths for data transmission.
- Avoiding Bottlenecks:
By rerouting data to avoid congested paths, Adaptive Routing helps prevent bottlenecks, ensuring smoother data flow.
SHIELD ( Self-Healing Interconnect)
It is designed to provide high-performance entertainment experiences, including streaming video, gaming, and smart home integration. Below are the key features and components of NVIDIA SHIELD:
Streaming Media Player:
- 4K HDR Streaming: SHIELD supports 4K HDR content, providing stunning video quality for streaming services like Netflix, Amazon Prime Video, Disney+, and more.
- AI Upscaling: It features AI-enhanced upscaling technology that can improve the quality of HD video content to near 4K resolution.
Gaming:
- Cloud Gaming: NVIDIA SHIELD supports GeForce NOW, NVIDIA’s cloud gaming service that allows users to stream a vast library of PC games directly to the device.
- Android Gaming: It also supports Android games, giving users access to a wide variety of titles from the Google Play Store.
- GameStream: Users can stream games from their GeForce-powered PC to their SHIELD device with low latency, effectively turning their SHIELD into a powerful gaming console.
Smart Home Integration:
- Google Assistant: SHIELD comes with built-in Google Assistant, enabling voice control for searching content, controlling smart home devices, and accessing various services.
- SmartThings Hub: It can act as a SmartThings hub, allowing users to control compatible smart home devices directly from the SHIELD.
GPUDirect RDMA (Remote Direct Memory Access)
GPUDirect RDMA is an NVIDIA technology that enables direct communication between GPU memory and third-party devices (e.g., network adapters, storage devices) without involving the CPU.
Key Features:
- Direct Data Transfer: Enables direct transfers between GPU memory and remote devices, bypassing the CPU.
- Reduced Latency: Minimizes data transfer latency, crucial for real-time applications.
- Improved Bandwidth: Leverages high-speed interconnects for higher throughput.
- Enhanced Scalability: Supports multi-GPU and multi-node configurations for large-scale parallel computing.
- Compatibility: Works with technologies like InfiniBand and RoCE.
Network topology design
Support multiple network topologies
● Fat-Tree/DragonFly+
Image Source:NVIDIA
● Fat-Tree vs DragonFly+
| Fat-Tree | Dragonfly+ | |
| Applicable cluster size (non-blocking) | Unlimited |
>800 nodes (For HDR) >2K nodes (For NDR) |
| Network cost | High | Moderate |
| Advantages |
a.Simple networking b.Network balance, simple routing algorithm c.No risk of Credit loop deadlock |
a. Low cost (saving switches and cables) b.Flexible networking, easy to expand, suitable for phased construction |
| Applicable scenarios | Unlimited |
a.Large clusters built in phasesb. b.Supercomputing cloud, multi-tenant sublease model cluster |
| Current status of industry applications | Most widely used, with the highest market share | Domestic supercomputing customers have just started to practice DF+ |
Conclusion
NVIDIA InfiniBand has emerged as a critical technology for high-performance computing, offering unparalleled speed, low latency, and efficient data transfer. Understanding the basics of InfiniBand enables organizations to optimize their data centers and achieve superior network performance.
For those looking to invest in high-quality networking equipment, Router-switch.com is a trusted resource. Renowned for offering top-notch products at competitive prices for 22 years, like nvidia infiniband switches. We ensure to offer reliable and cost-effective solutions for your networking needs.

Expertise Builds Trust
20+ Years • 200+ Countries • 21500+ Customers/Projects
CCIE · JNCIE · NSE7 · ACDX · HPE Master ASE · Dell Server/AI Expert