In the realm of computer networking, the concept of layering was developed to adapt to the ever-evolving technology landscape. Each layer in a networking model has a distinct function, passing information up and down to the subsequent layer as data undergoes processing.
The OSI Network Model Standard
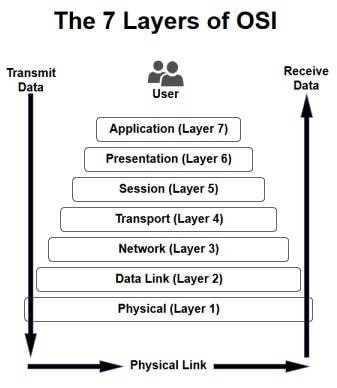
The OSI (Open System Interconnection) network model comprises seven layers, with each layer serving a unique role in the network hierarchy.
- Physical Layer: Responsible for the hardware-level communication services of an application.
- Data Link Layer: Governs data transfer on a single link.
- Network Layer: Defines end-to-end packet transport, logical addresses, routing implementation, and learning routes.
- Transport Layer: Manages error recovery and multiplexes application data streams on the same host.
- Session Layer: Focuses on session establishment, control, and termination, including management of bidirectional messages.
- Presentation Layer: Defines data format and encryption.
- Application Layer: Manages communication services for applications.
Understanding the Session Layer
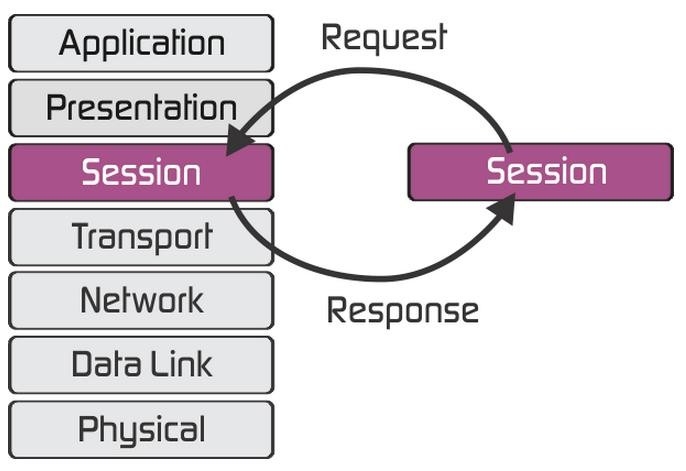
The session layer, the fifth layer in the OSI model, builds on the transport layer’s services. It enables applications to establish and maintain sessions and synchronize them. By utilizing checkpoints, the session layer allows communication sessions to resume from the checkpoint in case of communication failure, which is particularly crucial for sending large files.
Functions of the Session Layer
- Establishing a Connection: To establish a session connection for two peer session service users, several tasks are performed:
- Mapping the session address to the shipping address.
- Selecting required Quality of Service (QoS) parameters.
- Negotiating session parameters.
- Identifying each session connection.
- Transmitting limited transparent user data.
- Data Transfer Phase: This phase focuses on organized and synchronized data transmission between two session users. The user data unit is the SSDU, and the protocol data unit is the SPDU. Data transmission between session users involves converting the SSDU into the SPDU.
- Connection Release: Connection release is accomplished through various functional units, including ordered release, discarded, and limited transparent user data transfer.
Session-Level Standards
To enable functional negotiation during the session establishment phase and facilitate reference by other international standards, twelve functional units are defined. Each system can select a subset of session services based on its unique needs and circumstances, allowing flexibility and customization.
Session Layer Protocols
Several session layer protocols are used in networking. Here are some popular ones:
- ADSP (AppleTalk Data Stream Protocol)
- ASP (AppleTalk Session Protocol)
- H.245 (Call Control Protocol for Multimedia Communication)
- ISO-SP (OSI session-layer protocol, e.g., X.225, ISO 8327)
- iSNS (Internet Storage Name Service)
- L2F (Layer 2 Forwarding Protocol)
- L2TP (Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol)
- NetBIOS (Network Basic Input Output System)
- PAP (Password Authentication Protocol)
- PPTP (Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol)
Exploring Networking Solutions at Router-switch.com
To dive deeper into the world of networking and unlock the full potential of your network infrastructure, visit Router-switch.com. Our platform offers a comprehensive selection of networking products and solutions tailored to your unique requirements.
Read More:
Expand Your Business Horizons by Becoming a Supplier of Router-switch.com
The Shifting Landscape of the External Storage Market: Insights from Gartner