What is GPON? & How does GPON Work?
Gigabit Passive Optical Networks (GPON) is a fiber optic technology that enables faster data transmission and reception over a single cable. Optical fiber to the home or building will be possible with a point-to-multipoint architecture. It was created in response to the need to improve copper networks and offers access to video, voice, and data.
A GPON system consists of an optical line terminal (OLT) that uses a passive optical distribution network to connect many optical network terminals (ONTs/ONUs) (ODN).
GPON supports:
- Triple-play (VoIP, Data, and IPTV) services provide cost-effective all-services solutions.
- Higher data rates and transmission bandwidth
- Coverage on a large scale
- Data encryption and increased security (supports block length of 128 bits and key lengths of 128, 192, and 256 bits.)
- All types of Ethernet protocols
It is a widely used choice among major telecom companies all around the world. And people choose GPON over other technologies because it allows them to integrate various services into a single fiber transport network.
What’s the fundamental of GPON?
Ethernet, TDM (Time Division Multiplexing), and ATM traffic can all be sent over a GPON network. OLTs (Optical Line Terminals), ONUs (Optical Network Units), and a splitter make up a GPON network. When the signal is split, the splitter divides it. The OLT receives all optical signals from ONUs in the form of light beams and converts them to electrical signals.
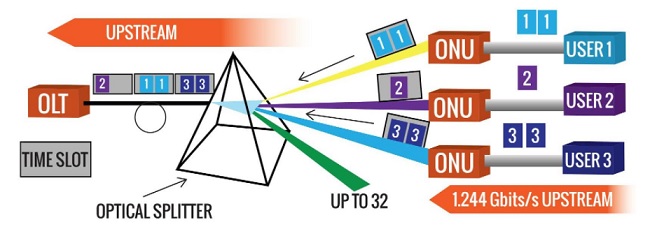
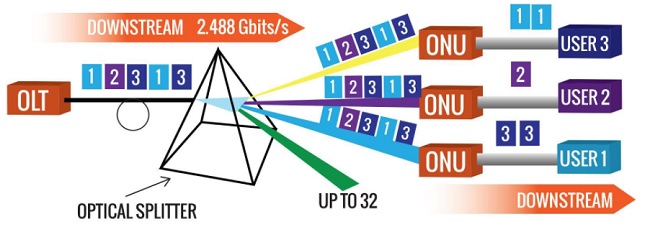
In most cases, OLTs can accommodate up to 72 ports. End users are connected to an ONU, which sends their signals back to the OLT. A GPON network can cover up to 20 kilometers and serve up to 64 users. GPON uses Optical Wavelength Division Multiplexing to use both upstream and downstream data (WDM).
The wavelength of the lasers in the downstream transmission is 1490 nm, whereas the wavelength in the upstream transmission is 1550 nm. A single-mode optical cable from the central office is routed to a passive optical power splitter near the end-users. After that, the optical splitter divides the electricity into two to sixty-four independent pathways. Separate single-mode fiber strands will travel directly from the optical splitter to the end user’s house, company, school, etc.
This transmission can travel up to 20 kilometers from the central office to the user. Different bit rates are available with GPON transmitting downstream in a broadcast method and upstream in a TDMA (time division multiple access) manner, with 1.2 Gbit/s in upstream and 2.4 Gbit/s in downstream being the most frequent.
How does GPON work?
GPON is a point-to-multipoint access network. The use of passive splitters in the fiber optic distribution network (ODN) is GPON’s most distinguishing feature. This allows an Internet service provider (ISP) to serve several residences or businesses with a single feeding fiber. Fiber optics refers to the use of cables to transfer light in fiber optic technology.
We’ll use the optical line terminal (OLT) at your Internet service provider’s (ISP) headquarters as the GPON system’s start point in this example.
- Your ISP’s Internet, voice/telephone, and TV data services are all sent from this point.
- Until it reaches the passive optical splitter, this data flows over the single-fiber optical distribution network (ODN).
- Once the data reaches the splitter, the splitter divides the light signal into several signals, which are then distributed to separate ONT/ONU devices on your home or business premises to give you access to these services. The ONT/ONUs are the final destinations.
Conclusion
The basic working steps of GPON are as follows:
OLT sends one-point signal > ODN > splitter breaks into multiple signals > multiple ONT/ONUs receive signals.
This is a simplified form, but it provides you with a general concept of how a GPON system works. GPON offers a wide range of advantages that allow for quick, flexible, mass-market fiber deployments at the lowest feasible cost of ownership and deployment. If you want to order Huawei OLT products, welcome to visit: Shop Optical Access Network at Router-switch.com .
Explore Optical Access Network Products:
Related Topics:
What is the Difference Between OLT and ONT?
What’s the OLT/Optical Line Terminal?