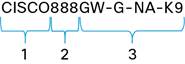
Do you know the rules of naming the Cisco 800 Series Integrated Services Routers (ISRs)? How is the name for the popular Cisco 800 Series routers put together?
The Cisco 800 series is a so big family that contains so many different router models designed for small branch offices or small businesses. And the most popular series is the Cisco 880 series.
Note: Most of Cisco 800 series routers and models have been announced End-of-Sale and End-of-Life. The latest and previous End-of-Life and End-of-Sale Notices you can read here: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/products/routers/800-series-routers/eos-eol-notice-listing.html
More and detailed info about the Cisco 800 Series Routers you can read here: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/products/routers/800-series-routers/index.html
Compare Models: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/products/routers/800-series-routers/models-comparison.html
In this article we will decode the names of the Cisco 800 series routers, which may help you know your Cisco branch routers well, and even help you find or select the very right one for your business.
Let’s go, look at the Cisco ISR Naming first.
1. Prefix
“CISCO” = Standard product ID (PID) prefix
“C” = Shortened prefix identifying slight product variation (that is, fan vs. fan-less, lead vs. lead-free (to comply with Reduction of Hazardous Substance 6 – lead [RoHS6])
2. Product Number
The second digit of the number section identifies the positioning and performance:
● “810” = Machine-to-machine gateways (that is, for ATMs)
● “850” = Older Cisco 800 Series Integrated Services Routers (ISRs), replaced by Cisco 860 Series ISRs
● “860” = Current entry-level Cisco 800 Series ISRs; single WAN interface
● “870” = Older Cisco 800 Series ISRs, replaced by Cisco 880 Series ISRs
● “880” = Current midrange Cisco 800 Series ISRs; WAN + Wireless WAN backup (Cisco 880G ISR)
● “890” = Current high-end Cisco 800 Series ISRs; 2 * WAN (active/active or active/standby)
The third digit identifies the primary WAN interface:
● “8×1” = RJ-45 Ethernet WAN interface
● “8×6” = DSL-over-ISDN WAN interface (very-high-bit-rate DSL/asymmetric DSL2 [VDSL/ADSL2] + Annex B)
● “8×7” = Basic telephone service WAN interface (VDSL/ADSL2 + Annex A), which allows splitter
● “8×8” = Basic telephone service WAN interface (G.SHDSL), which does not allow splitter
● “8×9” = Wireless WAN interface
Exceptions with multiple primary WAN interfaces follow:
● “86xVAE” = 1 * Ethernet and one identified by the third number (6 or 7): Both are physically present,
but just one can be active at a time
● “891” = 1 * Gigabit Ethernet, 1 * Fast Ethernet, and one v.92
● “892” = 1 * Gigabit Ethernet, 1 * Fast Ethernet, and one ISDN backup (not ISDN DSL)
3. Product Capabilities
Security:
● “K9” = Security router
● “SEC-K9” = Security router with Advanced IP Services
Wireless LAN:
● “W-A” = Router with 802.11n Wireless FCC compliance
● “W-E” = Router with 802.11n Wireless ETSI compliance
● “W-N” = Router with 802.11n Wireless Hong Kong, India, and Australia compliance
● “W-P” = Router with 802.11n Wireless Japan compliance
● “WD-A” = Router with dual and concurrent 2.4- and 5-GHz frequencies with FCC compliance
● “WD-E” = Router with dual and concurrent 2.4- and 5-GHz frequencies with ETSI compliance
● “WD-N” = Router with dual and concurrent 2.4- and 5-GHz frequencies with Hong Kong, India, and
Australia compliance
● “GN” = 802.11g- and 802.11n-capable
Note: The nomenclature “GN” was inserted at the beginning of Wireless n; therefore, newer products do not have it but are still 802.11n-capable.
Wireless WAN:
● “G” = Router with third-generation (3G) capabilities (older; carrier type was selected at ordering)
● “G-S” = Router with 3G for Sprint networks
● “G-V” = Router with 3G for Verizon networks
● “G-A” = Router with 3G for North America Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM) networks
● “G-U” = Router with 3G for universal 3.5G High-Speed Packet Access (HSPA) networks
● “G-B” = Router with 3G for Bharat Sanchar Nigam Limited (BSNL) networks
● “G+7”= Router with 3.7G HSPA+ Release 7 universal networks
● “G+7-A” = Router with 3.7G HSPA+ Release 7 AT&T networks
● “4G”* = Router with fourth-generation (4G) capabilities (LTE 1.0 or LTE 2.0)
● “LTE”* = Router with 4G capabilities (always LTE 2.0)
● “4G-V” = Router with 4G LTE 1.0 for Verizon
● “4G-A” = Router with 4G LTE 1.0 for North America GSM
● “4G-G” = Router with 4G LTE 1.0 for universal networks (except Canada, Japan, and Australia)
● “[4G|LTE]-GA” = Router with 4G LTE 2.0 for universal networks and Australia
● “[4G|LTE]-VZ” = Router with 4G LTE 2.0 for Verizon
● “[4G|LTE]-ST” = Router with 4G LTE 2.0 for Sprint
● “[LTE]-LA” = Router with 4G LTE 2.5 for Latin America (LATAM) and Asia-Pacific (APAC)
● “[4G|LTE]-NA” = Router with 4G LTE 2.0 for North America (AT&T and Canada)
● “[4G|LTE]-MNA” = Router with 4G LTE 2.0 for Multicarrier North America (AT&T, Sprint, Verizon, and Canada)
● “[4G|LTE]-JP” = Router with 4G LTE 2.0 for Japan
● “HG” = Hardened router if the G has “H” prepended
* “4G” and “LTE” can be considered synonyms with no technical differences.
DSL:
● “V” = Router with VDSL+
● “A” = Router with ADSL+
● “M” = Router with Annex M support
● “J” = Router with Annex J support
● “B” = Router supports bonding of DSL lines
Voice:
● “CUBE”= Router with integrated Cisco Unified Border Element (CUBE) license
● “-V” = Router with voice gateway capabilities (newer platforms)
● “SRST” = Router with Survivable Remote Site Telephony (SRST) capabilities; older platforms
EFM/ATM:
● “E” = Router with Ethernet in the First Mile (EFM) support (Exception: VAE; see under “Other”)
● “EA” = Router with EFM and ATM support
Other:
● “VAE” = Router with multiple WAN interfaces (VDSL+, ADSL+, and Ethernet)
● “F” = Router with Small Form-Factor Pluggable (SFP) and RJ-45 combination port (on just the first
Cisco 890 platforms; newer Cisco 890 platforms have it as well, without the “F” in the name)
● “FSP” = Router with “F” (as previously) plus higher performance, positioned for service providers
The product capabilities are aligned in the following order:
[Hardened] [Primary Interface attributes] [WWAN] [WLAN] – [WWAN attributes] – [WLAN attributes] – [k9]
The Naming Explanation for Cisco 800 Series from https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/products/collateral/routers/800-series-routers/qa_c67-716652.html
More Related Cisco 800 and Cisco 880 Topics…
Cisco 890 Series ISR Info Update 2015