The Root Bridge
In STP configured switched LAN or broadcast domain, a switch is designated as the root bridge. The root bridge serves as an administrative point for all spanning-tree calculations to determine which redundant links to block. An election process determines which switch becomes the root bridge.
Each switch has a Bridge ID (BID) that is made up of a priority value, an extended system ID, and the MAC address of the switch.
All switches in the network take part in the election process. After a switch boots up, it sends out BPDU frames containing the switch BID and the root ID every 2 seconds. By default, the root ID matches the local BID for all switches on the network. The root ID identifies the root bridge on the network. Initially, each switch identifies itself as the root bridge after boot up.
Let’s look at it this way, when switches A, B, C and D are on the same network or broadcast domain boots up, the switches will forward their Bridge Protocol Data Unit (BPDU) frames to neighboring switches. All switches in the network or broadcast domain will read the root ID information from the BPDU frame of all their neighbors. After reviewing the entire root ID’s from the BPDU received from each switch, the switch with the lowest BID ends up being identified as the Root Bridge for the spanning tree process. It may not be an adjacent switch, but any other switch in the broadcast domain.
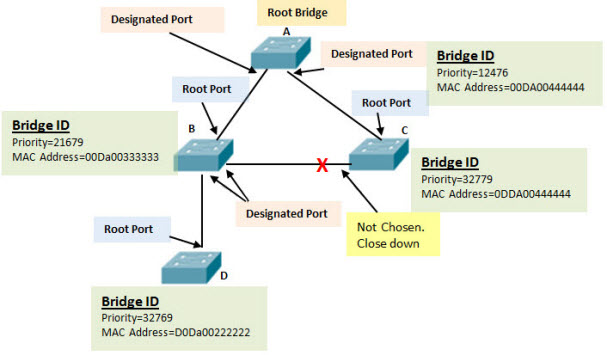
Study the figure below and see if you can identify the switch with the lowest priority.
Root Ports–Switch ports closest to the root bridge with the lowest cost path.
Designated Ports–All non-root ports that are still permitted to forward traffic on the network.
Non-designated Ports–All ports configured to be in a blocking state to prevent loops.
So we got these:
*Each switch has a bridge ID (BID) of priority value followed by MAC address
*Switches exchange Bridge Protocol Data Unit (BDPU) to compare bridge IDs
*The switch with the lowest bridge ID becomes the root bridge.
*Eventually, all switches agree that the switch with the lowest BID is the root bridge.
—Original reading from orbit-computer-solutions.com
More Related Network Tips:
Root Port Selection on a Switch