 Advances in flash technology—including the use of QLC-based flash, TCP/IP-based NVMe, and dedicated NVMe drives with onboard computing capabilities—are extending the applicability of flash to extreme performance and cost-sensitive use cases.
Advances in flash technology—including the use of QLC-based flash, TCP/IP-based NVMe, and dedicated NVMe drives with onboard computing capabilities—are extending the applicability of flash to extreme performance and cost-sensitive use cases.
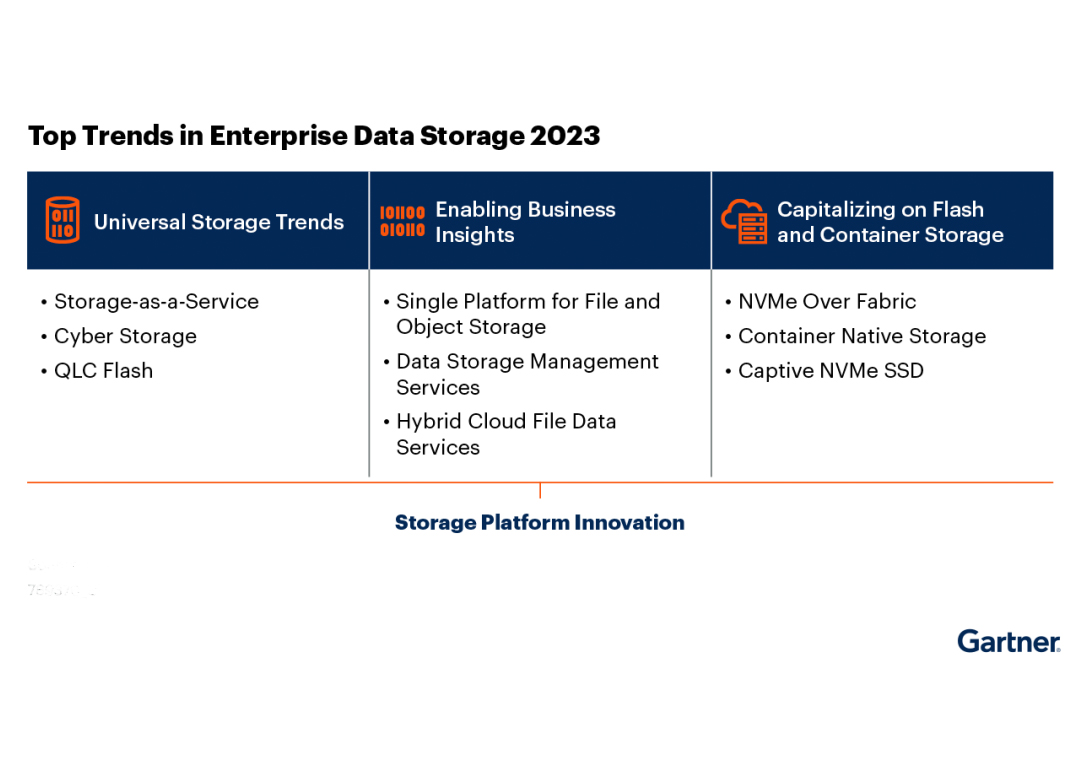
 Common trend: QLC all-flash will replace hybrid storage
Common trend: QLC all-flash will replace hybrid storage
Strategic Assumption: Enterprises will use QLC in 25% of SSD flash media by 2027, up from 5% by the end of 2022.
Description: Quad-level cell (QLC)-based storage arrays employing software-enabled ASIC or FPGA logic (to overcome lifetime constraints, increase endurance, and performance) are currently being deployed for general-purpose block storage use cases. They are also deployed in backup and disaster recovery use cases where the performance of replacing arrays of TLC media devices is not as critical. QLC-based storage arrays are increasingly being used to replace HDD disk arrays in file and object use cases such as analytics, backup, and disaster recovery. QLC-based arrays are gaining popularity for very high-density, multi-byte use cases.
Why it’s trending: To take advantage of the benefits of low-cost flash media for a wider range of application needs, storage vendors are using software and custom logic to overcome the limitations of QLC media. The cost delta advantage of QLC versus triple-level cell (TLC)-based arrays, combined with increased durability and performance, provides enough long-term benefits for enterprises (for example, fast recovery of backup data in the event of recovery from a ransomware incident).
Impact: As the growth of unstructured data drives the need for higher density SSD drives, QLC-equipped arrays have the potential to replace an increasing number of TLC-based flash arrays and hybrid HDD arrays. The net impact on the cost of traditional hybrid HDD arrays is a decline in market share, while the growth of unstructured data is accelerating. This effect will lower the average selling price of general-purpose block storage arrays while increasing the average selling price of object storage arrays.
Action:Customers should re-evaluate their application infrastructure environments based on use case and workload requirements and determine the overall price and performance benefits of using QLC-based storage versus hybrid HDD and TLC-based storage.
Block Storage Trends: Enabling NVMe Through Fabric
Strategic Assumption: By 2027, 25% of enterprise organizations will deploy NVMe-oF as a storage networking protocol, up from less than 10% by mid-2023.
Description: NVMe-oF is a networking protocol that takes advantage of the parallel access and low latency of NVMe Peripheral Component Interconnect Express (PCIe) devices. NVMe-oF tunnels NVMe commands to remote subsystems. The specification defines a protocol interface intended for use with high-performance fabric technologies, including Remote Directory Memory Access (RDMA) over Fiber Channel, InfiniBand, or Ethernet with RoCE v2, iWARP, or TCP. This provides a front-end interface to the storage system, scales to a large number of NVMe devices, and extends the access distance of NVMe-enabled subsystems within the data center. NVMe-oF can significantly improve data center network latency.
Why it’s trending: NVMe-oF products address use cases where low-latency application requirements combined with NVMe drives are critical. While infrastructure changes and upgrades are required, the clear benefits these technologies can bring are attracting the need for high performance and the use of scalable architectures that can take advantage of underlying networking capabilities combined with NVMe flash media. The architecture provided by the NVMe-oF protocol scales and enhances storage capabilities in distributed disaggregated platforms.
Impact: The NVMe-oF protocol accelerates the adoption of next-generation storage architectures such as disaggregated storage-compute that independently scales capacity and compute, the use of software-defined storage, and hyper-converged and composable infrastructure. Of the NVMe-oF options, NVMe-TCP has the greatest advantage because within the enterprise, the cost and simplicity of Ethernet can meet the bandwidth requirements of iSCSI and low-end Fiber Channel SANs below 16Gbps. Additionally, NVMe-oF can scale to high capacity levels with high availability features and can be managed from a central location to serve dozens of compute customers.
Action: Identify which workloads require the scalability and performance of NVMe and NVMe-oF-based solutions to justify the premium cost of such deployments. Use it for high-performance applications such as AI/mobile computing, high-performance computing, in-memory databases, transaction processing or as an alternative to iSCSI environments where managed STaaS can be used. Identify potential storage platform, network interface controller, host bus adapter, and network fabric vendors to verify interoperability testing and reference materials are available.
Emerging Trend: Dedicated NVMe SSDs
Strategic Assumption: By 2026, dedicated NVMe SSDs will replace over 30% of internal deployed capacity, a significant shift from the less than 5% seen in mid-2023.
Insight: Captive NVMe SSDs integrate processor cores, greatly enhancing onboard computational power and enabling in-drive I/O processing. Replacing standard SSDs, they offer storage system-level functionalities, boosting application capabilities across a wide spectrum. Captive NVMe SSD vendors, starting with NAND design, optimize storage environments through software. The primary function is to offload storage controller CPU I/O.
Rationale: Storage is increasingly seen as a strategic lever to solve and enable critical storage system functionalities. Leveraging vendor procurement and integration of compute and analytic capabilities, Captive NVMe drives add relative intelligence to optimize drive intelligence across key operational factors. Future enhancements will greatly reduce hardware management and support costs, enhancing data management through advanced AIOps capabilities. These drives pave the way for more efficient, scalable storage system architectures like software-defined disaggregated storage-computing, furthering NVMe-TCP adoption.
Impact: Utilizing dedicated NVMe SSDs yields numerous potential benefits, including enhanced storage operations, cost savings, network resilience, and intelligent data storage service environments. The vendor-built NVMe SSD approach requires significant internal engineering and procurement expertise, necessitating strategic acquisition of next-gen NAND technology and scale to compete effectively with vertically integrated NAND/SSD vendors. Downsides to proprietary NVMe SSDs include increased risk associated with single-source supply, impacting storage system-level availability and transition costs during supply changes.
Dedicated NVMe SSDs boast these advantages through specialized logic and complex AI/ML algorithms:
Cost advantage of using low-latency NAND flash like QLC
Higher SSD density compared to standard SSDs
Additional compute capabilities for stronger SSD functionality and performance
Efficient computation abilities, such as compression and deduplication
Granular flash management, enhancing durability and resilience with limited over-provisioning
More efficient, flexible horizontal expansion of block storage architecture
Advanced network resilience features like media-level filtering, searching, and scanning
Real-time entropy change statistics of stored data (enhancing security)
Enhanced NVMe application-aware end-to-end security features
Improved power usage to offset carbon emissions and intelligent power and cooling features
Action Items:
Evaluate the role of built-in NVMe SSDs in your storage system and assess whether these advantages are crucial to the overall vendor selection process.
Take a proactive approach to assess how vendors meet tactical and strategic NVMe SSD requirements and how their strategies address future storage system trends.
Conduct thorough due diligence on risks and dependencies that could negatively impact purchases and ongoing supply requirements for critical application infrastructure needs.
Inquire with exclusive NVMe SSD vendors about their long-term views and commitments to roadmaps and robust procurement teams.
Ready to embrace the future of storage? Elevate your system integration game with cutting-edge Dedicated NVMe SSDs. Explore Router Switch for top-notch products and reshape your storage solutions today!
Check More Router Switch Products:
Read More:
Igniting the Future of ICT: An Invitation to Router-switch.com’s InnovateTech Speaker Program
How to Choose Server Configurations: Expert Tips for Beginners

