
Recently, O-RAN is popular in the market of access network.
As a new technology architecture that was born less than two years ago, the rise of O-RAN is indeed amazing, attracting widespread attention.
So, what exactly is O-RAN? What is the feature? Why are more and more manufacturers chasing this technology?
In this post, we will discuss this topic.
RAN, D-RAN, X-RAN and C-RAN
To explain short, the RAN is the radio access network. Before the advent of the 5G era, the base station (RAN) consisted of three parts: an antenna, an RRU (radio remote unit), and a BBU (baseband processing unit). The RRU is used to transmit and receive signals, and the BBU is used to process signaling messages.
First of all, let’s make a brief review of the history of the wireless access side.
In the 1G and 2G era, equipment such as BBU, RRU and power supply unit were placed in a cabinet, which was very bloated.
In the 3G era, distributed base stations were proposed. That is, the BBU and the RRU are separated, and the RRU can even be hung under the antenna without being placed in the same cabinet as the BBU. This is called D-RAN (Distributed Radio Access Network). With the development of technology (a main reason is that operators maintain a high cost…), C-RAN came into being.
What is C-RAN? It is Centralized RAN, which can also refer to Cloud-RAN, means centralized wireless access. Or take the BBU and RRU separation scheme, but the RRU is infinitely close to the antenna, which greatly reduces the attenuation through the feeder (the connection between the antenna and the RRU); at the same time, the BBU migrates and concentrates on the CO (central equipment room) to form the BBU baseband pool; The CO and the RRU are connected through a preamble network. This is very beneficial to inter-cell collaborative work, reducing the attenuation caused by transmission and saving costs.
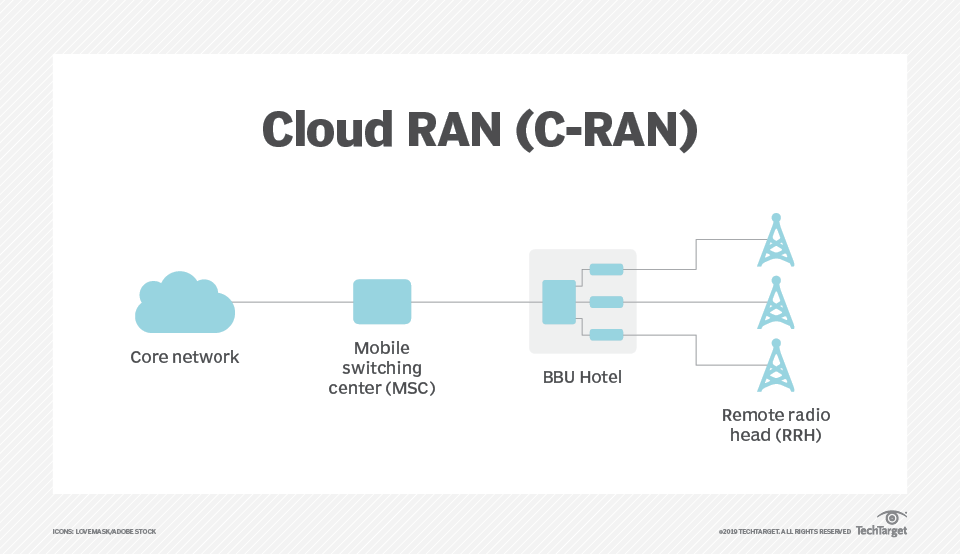
(Image from searchnetworking.techtarget.com)
Worldwide operators are also constantly exploring more advanced network architectures. In 2016, AT&T led a number of operators to form the x-RAN alliance with the goal of replacing traditional hardware-based RANs with open, replaceable, standardized equipment. The consortium focuses on three aspects: coupling the RAN control plane to the user plane, building a modular eNodeB software stack using COTS hardware, and exposing the south and northbound interfaces.
X-RAN and C-RAN are generally considered to be the predecessors of O-RAN.
In June 2018, the O-RAN Alliance was formally established, and was jointly initiated by 12 operators including China Mobile, AT&T, Deutsche Telekom, Japan NTT DOCOMO, and France Orange. The O-RAN Alliance expands the work and goals of the existing C-RAN Alliance to promote the evolution of the wireless access network toward a more open and intelligent direction.
But why should the O-RAN alliance be established?
How was O-RAN born?
Wireless network construction has always been the most important part of the carrier’s network total cost (TCO), accounting for roughly 60% to 70%. Most operators have just experienced huge investment in 4G networks and will face the pressure of investment in 5G networks.

5G network is different from 4G network. 5G network has fast speed, large bandwidth and high frequency band. That is to say, the penetration of 5G network will be far worse than that of 4G network. Explain in a popular way, the original 4G network covers only one base station in a certain area, while the 5G network coverage requires five base stations.
At the same time, the 5G network is a network that operators must invest. Large-scale network construction is bound to bring great cost. At this time, it is necessary to introduce new technologies and new solutions, and reduce the construction difficulty and reduce wireless network investment through program innovation.
In the context of the slowdown in “wireless Internet” traffic revenue growth and voice revenue decline, the vertical industry is the “blue ocean market” that operators must enter. Expanding the profitability of operators will be the primary task of 5G networks. New business in the vertical industry means more types of business, more complex network management, more efficient resource management solutions and a more flexible network architecture to facilitate business innovation.
In this context, the O-RAN industry alliance led by operators emerged as the times require, and proposed two core visions of “open” and “smart”.
The core of O-RAN: standardization + open source

(Image from https://www.o-ran.org/)
The ORAN Alliance is led and initiated by operators. There are three key principles:
- Guides the evolution of the industry. One is an open interface that supports interoperability of devices from different vendors. The other is to build wireless connections through virtualization. Network access to achieve intelligent wireless networks based on big data.
- To actively and fully utilize the common platform to reduce reliance on proprietary platforms.
- To develop and promote standardized definitions of interfaces and related APIs and explore open source solutions.
Explaining these three rules in plain language, O-RAN is promoting the following four directions: network intelligence, interface openness, hardware generalization and software open source. Equivalent to the hardware that was originally a black box, now all become a general-purpose standard product, and the software code becomes open source.
This may mean that in the future, a single manufacturer’s equipment in a certain existing network will not be irreplaceable; the seller does not need to package and purchase the hardware and software products of the same manufacturer, but fully utilizes the common platform and reduces the private platform. The reliance, development, advancement of interfaces and related API standardized definitions, and exploration of open source solutions also mean that “standardization” will become a trend.
With the opening of general-purpose hardware, the hardware will be generalized after the soft and hard decoupling of network functions, and the independence of operators will be higher, and it will no longer be dominated by equipment vendors. Traditional equipment vendors will face major changes, and some Internet companies, software vendors, IT vendors will become new players in the market.
In fact, some IT vendors have begun to look at it. At MWC 2019 Barcelona, Lenovo and China Mobile jointly demonstrated the world’s first 5G O-RAN product, which is the first in the industry to realize a 5G CU/DU device cloud solution with cross-node, multi-virtual machine and full software.

(Image from https://www.o-ran.org/)
Now do you understand the O-RAN? Welcome to leave your comment!
Related Topics:
9 Benefits that 5G Can Provide while 4G Can’t
11 Protocols of IoT You need to know
How to Help Wireless Customers Select the Right Wireless Solutions?




