The transmission network is an important part of the communication network. Without it, data communication is not possible between different devices on the network.
In this blog, we will discuss the main concepts of transmission network.
Transmission Network
The transmission network is a network used as a transmission channel, and is generally used under the switching network, the data network, and the support network to provide a signal transmission and conversion network, and belongs to the basic network of the above three types of networks.
Transmission networks generally study fiber optic cable, copper wire, signal amplifiers, interfaces, connectors, interface converters, microwave systems, PDH, SDH, WDM, ASON, and satellites.
The combination of the transmission network and the data network and the voice network is very close, and the distance from the telecommunication service is relatively far.
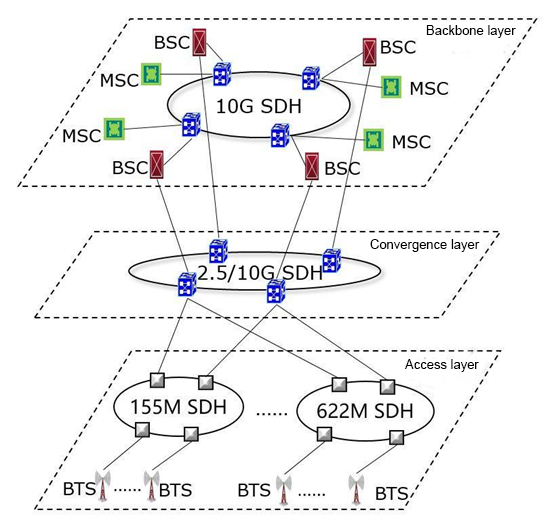
The following is a typical 2G mobile communication network transmission network architecture:
PDH (Plesiochronous Digital Hierarchy)
PDH, a quasi-synchronous digital series, was an early digital transmission system that began to emerge and developed rapidly in the 1980s.
PDH mainly has two series of standards:
- E1, PCM30/32 channel, 2.048Mbps, is adopted in Europe and China.
- T1, PCM24/ channel, 1.544Mbps, is adopted in North America.
There are some disadvantages of this PDH:
- There is no globally uniform standard
- Complicated structure and high cost
- Maintenance is difficult
SDH (Synchronous Digital Hierarchy)
SDH, Synchronous Digital Hierarchy, the synchronous digital series, is also a digital transmission system. It is a combination of fiber transmission technology and intelligent network technology.
The earliest proposed SDH concept was the American Bell Communications Institute, which was called Optical Synchronization Network (SONET).
In 1988, the International Telegraph and Telephone Consultative Committee (CCITT) accepted the concept of SONET and renamed it SDH.
Compared to PDH, SDH has the following advantages:
- Network management capabilities have been greatly enhanced.
- Unified standards and uniform specifications facilitate the interconnection of different manufacturers.
- Suitable for large capacity transmission.
- Proposed a new concept of self-healing network and enhanced protection.
- Byte multiplexing technology makes the upper and lower tributary signals in the network very simple.
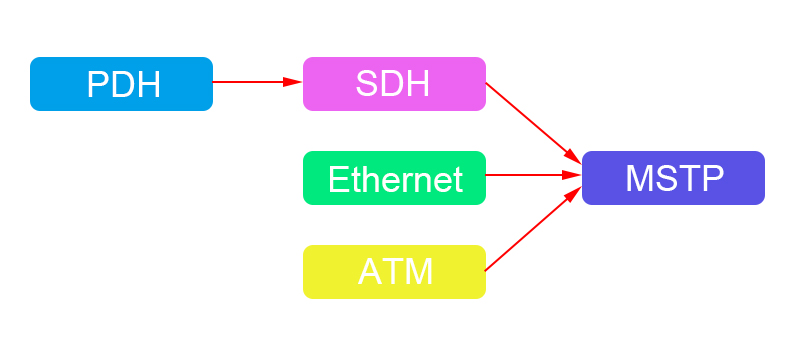
MSTP (Multi-Service Transmission Platform)
MSTP (SDH-based multi-service transport platform) refers to the multi-service node that provides unified network management for access, processing, and transmission of services such as TDM, ATM, and Ethernet based on the SDH platform.
The relationship of PDH, SDH and MSTP:
PTN (Packet Transport Network)
PTN refers to an optical transport network architecture and specific technology: a layer is set between the IP service and the underlying optical transmission medium, which is aimed at the burstiness and statistical recovery of packet traffic. Designed with the requirements of delivery, with packet services as the core and supporting multi-service provisioning, with lower total cost of ownership (TCO), while adhering to the traditional advantages of optical transmission, including high availability and reliability, efficient bandwidth management mechanisms and Traffic engineering, convenient OAM and network management, scalability, high security, etc.
WDM (Wavelength Division Multiplexing)
WDM is a technique that uses multiple lasers to simultaneously transmit multiple beams of different wavelengths on a single fiber. Each signal is modulated by its data (text, voice, video, etc.) and transmitted within its unique ribbon.
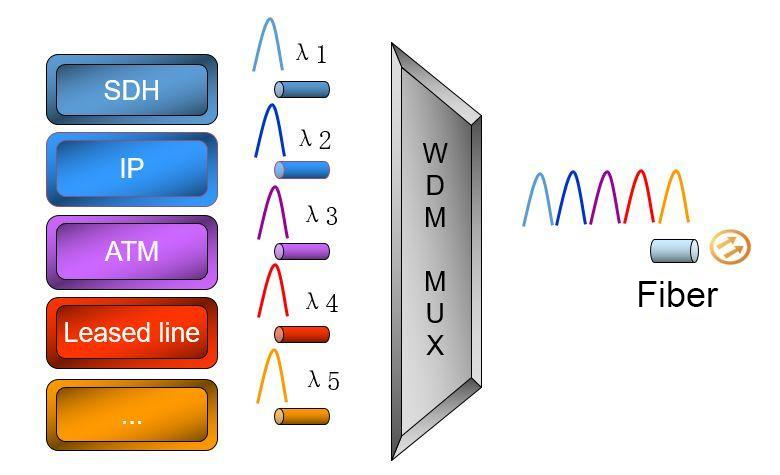
WDM can increase the capacity of existing fiber infrastructure for telephone companies and other operators. Manufacturers have introduced WDM systems, also known as DWDM (Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing) systems.
DWDM can support more than 150 different wavelengths of light waves for simultaneous transmission, and each beam of light can reach a data transmission rate of up to 10Gb/s. This system can provide data transmission rates of more than 1 Tb/s on a fiber optic cable that is thinner than the hair.
Optical communication is a way in which light carries signals for transmission. In the field of optical communications, people are accustomed to naming by wavelength rather than by frequency. Therefore, the so-called Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM) is essentially frequency division multiplexing.
WDM is a system that carries multiple wavelengths (channels) on one fiber and converts one fiber into multiple “virtual” fibers. Of course, each virtual fiber works independently at different wavelengths, which greatly increases the transmission capacity of the fiber.
Due to the economics and effectiveness of WDM system technology, it has become the main means of expanding the current fiber-optic communication network. As a system concept, WDM technology usually has three multiplexing modes, namely wavelength division multiplexing at 1 310 nm and 1 550 nm wavelength, Coarse Wavelength Division Multiplexing (CWDM) and dense wave. DWDM, Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing.
OTN (Optical Transport Network)
OTN is based on WDM technology. An optical transport network (OTN), a type of network, refers to a transport network that implements transmission, multiplexing, routing, and monitoring of service signals in the optical domain, and guarantees performance indicators and survivability.
OTN technology is the product of the compromise between electrical and all-optical networks. It transplants SDH’s powerful OAM&P concepts and functions into WDM optical networks, effectively offsetting the performance monitoring and maintenance management of existing WDM systems. insufficient.
OTN technology can support transparent transmission of customer signals, high-bandwidth multiplexing switching and configuration (minimum cross-grain is ODU1, about 2.5 Gbit/s), with powerful overhead support, powerful OAM function, and support for multi-layer embedded Set of Series Connection Monitoring (TCM) features with Forward Error Correction (FEC) support.
Huawei Transmission Network devices are the very hot products in the global market. If you’re interested, please visit our product lists of this series: Huawei Transmission Network Products.
Related Topics:
How Does Optical Fiber Transmit Signal?
Optical Communication Terminology Cheat Sheet
9 Concepts and 2 Principles that New to Telecommunication Need to Know


